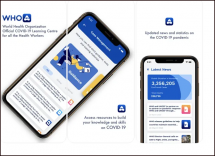
WHO COVID-19 Learning Resources Application
The WHO mobile learning app focuses on providing frontline health workers with critical, evidence-based information and tools to improve their skills and capabilities related to the pandemic.
This COVID-19 Digital Response offers up-to-the-minute guidance, training, and virtual workshops to support health workers in caring for patients infected by COVID-19, as well as how they can protect themselves as they do their critical work.
The app was created in direct response to an online survey of health workers conducted in March and April 2020 that received 20,000 submissions. Key features include learning guidance, learning materials, and tools organized into the following COVID-19 subject matter areas:
- Case Management: How to care for COVID-19 patients
- Infection Prevention Control: Protecting health worker and the community
- Risk Communication and Community Engagement: Communicating effectively with the public
- Epidemiology: Distribution, characteristics, and determinants of COVID-19
- Statistics: Updated news and statistics on the COVID-19 pandemic
- Laboratory: Testing for COVID-19 in humans
- Health Services and Systems: Strategic planning and coordinated action
- International Health Regulations: Public health and international spread of disease
- Research & Development: Working towards a treatment and a vaccine.
- Operational Support and Logistics
- Regional Information
The WHO mobile learning app is a convenient tool for accessing WHO’s rapidly expanding and evolving training materials and guidance, along with opportunities to participate in virtual classrooms and other live training in six global languages: Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian, and Spanish.
Last modified: July 21, 2020
Language: Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian, Spanish