COVID-19 Global Risk Communication and Community Engagement Strategy
There is an unprecedented need to elevate the role risk communication and community engagement (RCCE) plays in breaking the chains of transmission and mitigating the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Until biomedical tools such as vaccines or treatments are developed and widely available, people’s behaviour and their willingness to follow public health and social measures remain the most powerful tools to stop the spread of the virus.
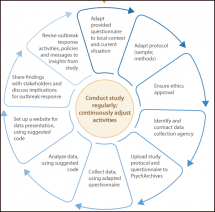
The COVID-19 Global Risk Communication and Community Engagement Strategy, December 2020 – May 2021 provides an important update for member states and supporting partners. The updated strategy is underpinned by a socio-behavioral trends analysis and builds on the learnings from the response to-date. The shift presented in the document is towards the community engagement and participatory approaches that have been proven to help control and eliminate outbreaks in the past.
The overarching goal of the strategy: That people-centred and community-led approaches are championed widely – resulting in increased trust and social cohesion, and ultimately a reduction in the negative impacts of COVID-19.
Last modified: January 4, 2021