WHO competency framework, risk communication and community engagement
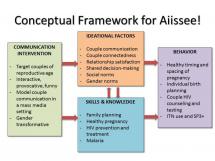
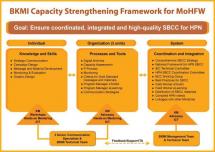
The risk communication and community engagement (RCCE) competency framework is a resource that details the essential behaviors and activities necessary for effective communication and engagement with communities before, during, and after public health emergencies. The purpose of this framework is to establish and promote a common understanding of behavioral competencies and how they should be applied for high-performing and community-centered health emergency programs. It is intended to support the development of standardized training programs, professional development, and talent acquisition and to enhance the capabilities of public health professionals involved in RCCE. Its goal is to inform the establishment of a skilled, well-trained RCCE workforce that consistently understands and executes the necessary behaviors and activities required to conduct RCCE activities with competence and professionalism.
Last modified: July 21, 2024
Language: English
Source: World Health Organization
Year of Publication: 2024